8 Hormones Every Woman Should Know For Her Fertility And Wellbeing
November 6, 2019 | Yesmom
Very few of us give adequate attention to our reproductive health till we start planning our pregnancies, find ourselves pregnant or have difficulty in getting pregnant. Taking care of ourselves and making healthy choices can help protect our reproductive system from infections, and injury. It may also help prevent long term health complications. If you become aware that your ovarian reserves are low, you can take proactive steps to freeze your eggs and insure your motherhood. So when you feel ready to be a mom, you can always use these eggs in case you are unable to get pregnant naturally.
Hormones play a major role in a woman’s health. It is vital to understand how hormone imbalance can affect your reproductive health and your general well being. Regular health check ups can help you in ensuring your hormones are in balance and to take remedial measures at the first sign of trouble. If your reproductive health gets affected, you may face difficulties in getting pregnant and carrying a baby to term successfully.
When it comes to checking fertility and maintaining reproductive wellbeing, there are more hormones to learn about apart from those monthly ones we have learned from school. To get pregnant soon or in the future, and to keep our reproductive system healthy, there are 8 hormones to keep our eyes on. When any of these hormones are too high or too low, their imbalance can cause many health challenges.
But don’t worry about how you can check them. YesMom’s Fertility Test includes an analysis of all 8 of these hormones and can provide you with necessary context around them to take actionable insights into what they mean for your overall health and fertility
The Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH), Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Estradiol (E2) help you to assess your ovarian reserves and track fertility. Prolactin and LH levels are often checked if you have menstrual irregularities. They should be within the normal range for regular menstruation and ovulation. Testosterone, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and free T4 are important for our reproductive health. These are measured for evaluating sexual problems or general health conditions regarding the reproductive system. Any irregularity in any of these hormones can impact your fertility in different ways.

Now, let’s take a closer look at these 8 hormones:
Anti-Mullerian Hormone
The Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) is a naturally occurring hormone in women that can be used to evaluate our ovarian reserve. In fact, testing AMH levels has now become the most preferred and useful way to measure ovarian reserve. The ovaries produce AMH based on the number of ovarian follicles a woman has. These follicles in the ovarian reserve contain the eggs that eventually mature and get released periodically.
Thus testing the AMH level helps measure how many follicles we have left in our ovaries. AMH is tested from the blood samples and the test results are not affected by the use of birth control medications. A 2017 study from Poland reveals that “Reduced levels of AMH may indicate reduced ovarian reserve, even if the woman has regular menstrual cycles and the levels of FSH and E2 are still normal.”
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) is responsible for the growth and maturation of the egg follicles and starting the ovulation. The pituitary gland produces FSH and releases it in the bloodstream. Any imbalance in the FSH level, too much or too little can affect fertility as this may inhibit the release of eggs for fertilization. To assess ovarian reserves, FSH levels are measured on the 3rd day of the menstrual cycle.
High FSH levels indicate a decreased ovarian reserve. As we age, our FSH levels increase and this indicates a decrease in our estrogen and progesterone production. So rising FSH levels are also considered an indicator of perimenopause and if the FSH levels stay consistently high and a woman has not had her period for a year, it is generally accepted that menopause has occurred. There are blood and urine tests for determining FSH levels though the test results will not be accurate if you are on hormonal birth control.
Estradiol
Estradiol (E2) is an important hormone that regulates the healthy functioning of sexual organs. It is a form of estrogen produced by the ovaries and the adrenal glands. Also known as 17-beta-estradiol, this hormone is required for the growth and development of sex organs including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and breasts. Estradiol is also responsible for the health and normal function of other sexual organs. This hormone also plays a vital role in controlling fat distribution in females.
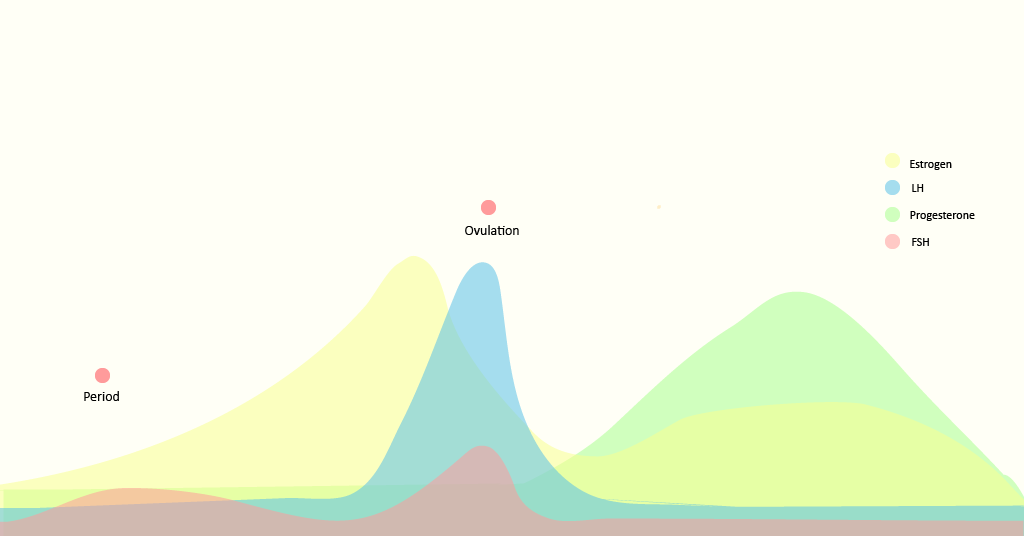
Estradiol tests are used for evaluating how well our ovaries are working. E2 levels are highest during ovulation as this enables the maturation and release of the eggs. During menstruation, E2 levels will naturally be at their lowest. Low estradiol levels may indicate that we are approaching menopause and we may be experiencing menstrual irregularities, hot flashes, and mood swings. On the other hand, too much estradiol can cause acne, constipation, loss of libido, weight gain and depression. It may also lead to infertility and increases our risk of uterine and breast cancer.
Prolactin
Prolactin is produced by the pituitary gland. It influences normal menstrual function and fertility. Prolactin is a hormone that stimulates milk production in new moms. It also pauses ovulation after the birth of the baby. Though it is known as the milk hormone, prolactin also has many other functions in the body, such as regulating the immune system and influencing behavior.
If we are not pregnant or lactating, our prolactin levels should be less than 25 ng/mL as increased prolactin levels in the blood may stop the production of estrogen in the ovaries. Blood tests can be used for finding out our prolactin levels, but the test will not be valid if we use birth control pills.
Luteinizing Hormone
The Luteinizing Hormone (LH) is produced by our pituitary gland. LH helps regulate the length of our menstrual cycle. It is the LH hormone that triggers ovulation and releases the mature egg from the ovary.
There is a sharp surge in ovulation 24-48 hours before ovulation. These are considered the two most fertile days of the menstrual cycle. The concentration of the LH hormone is measured in the urine. Keep in mind that the test results will not be reliable if we take birth control pills.
Testosterone
Testosterone is a steroid hormone that is found in both men and women. Blood tests can be used for testing testosterone levels. Though it is the main male hormone that regulates sperm production in men, women also need it in certain amounts for a variety of functions. Testosterone is involved in the growth, functioning, and maintenance of reproductive tissues. It helps in controlling sex drive, promoting muscle mass and increasing energy.
Excess of low levels of testosterone can affect fertility. If our estrogen level drops, our level of male hormones such as testosterone may increase and hormonal imbalance occurs. This can lead to menstrual irregularities, increased hair fall, male pattern baldness, acne, etc. Higher levels of testosterone are also seen in women suffering from Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is produced by our thyroid gland. It stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroxine and triiodothyronine which, in turn, are needed by the body for a variety of important functions. When thyroid hormones are too low in the body (hypothyroidism), the level of TSH goes up, indicating the need for more production.
Very low TSH value may indicate too much of thyroid hormones in the system (hyperthyroidism). Low levels of thyroid hormones can cause infertility as this interferes with egg release and ovulation. Other underlying causes of such as pituitary or immune system disorders can also affect fertility. TSH is usually checked using fasting blood samples.
Free T4
Free thyroxine (FT4) tests are conducted when TSH results are abnormal. Testing free T4 values can help in evaluating thyroid functioning and aid in diagnosing hyper/hypothyroidism. FT4 test is also recommended if you have an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter).
Even a slightly underactive thyroid can make it challenging for a woman to get pregnant. But, with proper treatment, these challenges can be dealt with successfully. Blood for testing Free T4 is best taken early in the morning, before having your meal. Be aware that the results may not be reliable if we are using birth control pills.
With the advance of modern medical technology and advanced egg freezing techniques, a woman can now choose to have children at much older ages than before. If you are planning to have a baby now or you want to know your options for postponing your choice of motherhood to a later date, it’s a good idea to get these hormone tests done to track your fertility.
Taking the Yesmom Fertility Test can help you have an informed discussion with your doctor as they will definitely insist on these tests if you are having any difficulty in getting pregnant. If you want to go in for egg freezing or IVF, these tests help assess and plan the treatment. Bear in mind that many of these test results may not be reliable if you are using birth control pills, as these medications alter the hormonal balance in your body. Whatever your choices are, make informed healthcare decisions and take charge of your own life and destiny.
https://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/anti-muellerian-hormone/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22646322
https://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/follicle-stimulating-hormone/
https://www.hormone.org/your-health-and-hormones/glands-and-hormones-a-to-z/hormones/luteinizing-hormone
https://www.health.harvard.edu/drugs-and-medications/testosterone–what-it-does-and-doesnt-do
htps://www.thyroid.org/thyroid-function-tests
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003718.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5509971/
https://www.menopause.org/for-women/menopauseflashes/menopause-symptoms-and-treatments/how-do-i-know-i’m-in-menopause-
https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/low-estrogen-symptoms#symptoms
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/news/story/4022/female-fertility-whats-testosterone-got-to-do-with-it.aspx